Python Note
Table of Contents
- Python Language
- Usages
- Misc
- 参考资料
python note.
<!– more –>
Python Language
Python 编程
for
for i in range(1,10,2): print(i) # output: 1 3 5 7 9 for i in [1,2,3]: print(i)
枚举类型
# 第一种方式 from enum import Enum Month = Enum('Month', ('Jan', 'Feb', 'Mar', 'Apr', 'May', 'Jun', 'Jul', 'Aug', 'Sep', 'Oct', 'Nov', 'Dec')) # 引用一个常量 print(Month.Jan) # 遍历枚举的所有成员: for name, member in Month.__members__.items(): print(name, '=>', member, ',', member.value) # 第二种方式 from enum import Enum, unique @unique class Weekday(Enum): Sun = 0 # Sun 的 value 被设定为 0 Mon = 1 Tue = 2 Wed = 3 Thu = 4 Fri = 5 Sat = 6 >>> day1 = Weekday.Mon >>> print(day1) Weekday.Mon >>> print(Weekday.Tue) Weekday.Tue >>> print(Weekday['Tue']) Weekday.Tue >>> print(Weekday.Tue.value) 2 >>> print(day1 == Weekday.Mon) True >>> print(day1 == Weekday.Tue) False >>> print(Weekday(1)) Weekday.Mon >>> print(day1 == Weekday(1)) True >>> Weekday(7) Traceback (most recent call last): ... ValueError: 7 is not a valid Weekday >>> for name, member in Weekday.__members__.items(): ... print(name, '=>', member) ... Sun => Weekday.Sun Mon => Weekday.Mon Tue => Weekday.Tue Wed => Weekday.Wed Thu => Weekday.Thu Fri => Weekday.Fri Sat => Weekday.Sat
Tips
enum 支持直到 python 3.4 版本才添加进来.低于 3.4 版本时,使用 enum 必须安装 enum34.
# 使用 pip 安装 pip install --upgrade pip enum34 # 使用 easy_install 安装 easy_install enum34
string
format
"{} {}".format("hello", "world") # 'hello world' "{0} {1}".format("hello", "world") # 'hello world' "{1} {0} {1}".format("hello", "world") # 'world hello world'
list to string
doc_content = ''.join(paragraph.text for paragraph in doc_file.paragraphs)
任意类型对象的打印
利用 str() 函数将对象转化为适于人阅读的形式,然后打印。
list
# -- 创建 List list1 = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000] list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ] # -- 访问列表的值 print "list1[0]: ", list1[0] print "list2[1:5]: ", list2[1:5] ## 输出结果: ## list1[0]: physics ## list2[1:5]: [2, 3, 4, 5] # -- 添加元素 list1.append(3000) # -- 删除元素 del list1[2] # -- 获取列表长度 len(list1) # -- 列表连接 print([1,2] + ["name","age"]) ## 输出结果: ## [1,2,"name","age"] # -- 列表扩展 aList = [123, 'xyz', 'zara', 'abc', 123]; bList = [2009, 'manni']; aList.extend(bList) print "Extended List : ", aList ; ## 输出结果: ## Extended List : [123, 'xyz', 'zara', 'abc', 123, 2009, 'manni'] # -- 判断是否包含某元素 print(3 in [1, 2, 3]) ## 输出结果: ## True # -- 列表截取 >>>L = ['Google', 'Runoob', 'Taobao'] >>> L[2] 'Taobao' >>> L[-2] 'Runoob' >>> L[1:] ['Runoob', 'Taobao'] # -- 遍历列表元素 for x in [1, 2, 3]: print x for i in range(0,len(xx_list)): print xx_list[i]
dict
增删改
dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'} dict['School'] = "RUNOOB" # 添加 dict['Age'] = 8 # 更新 del dict['Name'] # 删除键是'Name'的条目 dict.clear() # 清空字典所有条目 del dict # 删除字典
遍历 dict
for k,v in dict.items(): print("key:", k, "value:", str(v))
判断 key 是否存在
# python2 xx_dict.has_key(xx_key) # python3 xx_key in xx_dict
正则表达式
正则表达式模式
模式字符串使用特殊的语法来表示一个正则表达式:
字母和数字表示他们自身。一个正则表达式模式中的字母和数字匹配同样的字符串。
多数字母和数字前加一个反斜杠时会拥有不同的含义。
标点符号只有被转义时才匹配自身,否则它们表示特殊的含义。
反斜杠本身需要使用反斜杠转义。
由于正则表达式通常都包含反斜杠,所以你最好使用原始字符串来表示它们。模式元素(如 r'\t',等价于'\\t')匹配相应的特殊字符。
下表列出了正则表达式模式语法中的特殊元素。如果你使用模式的同时提供了可选的标志参数,某些模式元素的含义会改变。
| 模式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ^ | 匹配字符串的开头 |
| $ | 匹配字符串的末尾。 |
| . | 匹配任意字符,除了换行符,当 re.DOTALL 标记被指定时,则可以匹配包括换行符的任意字符。 |
| […] | 用来表示一组字符,单独列出:[amk] 匹配 'a','m'或'k' |
| [^…] | 不在[]中的字符:[^abc] 匹配除了 a,b,c 之外的字符。 |
| re* | 匹配 0 个或多个的表达式。 |
| re+ | 匹配 1 个或多个的表达式。 |
| re? | 匹配 0 个或 1 个由前面的正则表达式定义的片段,非贪婪方式 |
| re{ n} | 精确匹配 n 个前面表达式。例如,o{2} 不能匹配 "Bob" 中的 "o",但是能匹配 "food" 中的两个 o。 |
| re{ n,} | 匹配 n 个前面表达式。例如,o{2,} 不能匹配"Bob"中的"o",但能匹配 "foooood"中的所有 o。"o{1,}" 等价于 "o+"。"o{0,}" 则等价于 "o*"。 |
| re{ n, m} | 匹配 n 到 m 次由前面的正则表达式定义的片段,贪婪方式 |
| a | b | 匹配 a 或 b |
| (re) | G 匹配括号内的表达式,也表示一个组 |
| (?imx) | 正则表达式包含三种可选标志:i, m, 或 x。只影响括号中的区域。 |
| (?-imx) | 正则表达式关闭 i, m, 或 x 可选标志。只影响括号中的区域。 |
| (?: re) | 类似 (…), 但是不表示一个组 |
| (?imx: re) | 在括号中使用 i, m, 或 x 可选标志 |
| (?-imx: re) | 在括号中不使用 i, m, 或 x 可选标志 |
| (?#…) | 注释. |
| (?= re) | 前向肯定界定符。如果所含正则表达式,以 … 表示,在当前位置成功匹配时成功,否则失败。但一旦所含表达式已经尝试,匹配引擎根本没有提高;模式的剩余部分还要尝试界定符的右边。 |
| (?! re) | 前向否定界定符。与肯定界定符相反;当所含表达式不能在字符串当前位置匹配时成功 |
| (?> re) | 匹配的独立模式,省去回溯。 |
| \w | 匹配字母数字 |
| \W | 匹配非字母数字 |
| \s | 匹配任意空白字符,等价于 [\t\n\r\f]. |
\ S |
匹配任意非空字符 |
| \d | 匹配任意数字,等价于 [0-9]. |
| \D | 匹配任意非数字 |
| \A | 匹配字符串开始 |
| \Z | 匹配字符串结束,如果是存在换行,只匹配到换行前的结束字符串。c |
| \z | 匹配字符串结束 |
| \G | 匹配最后匹配完成的位置。 |
| \b | 匹配一个单词边界,也就是指单词和空格间的位置。例如, 'er\b' 可以匹配"never" 中的 'er',但不能匹配 "verb" 中的 'er'。 |
| \B | 匹配非单词边界。'er\B' 能匹配 "verb" 中的 'er',但不能匹配 "never" 中的 'er'。 |
| \n, \t, 等. | 匹配一个换行符。匹配一个制表符。等 |
| \1…\9 | 匹配第 n 个分组的子表达式。 |
| \10 | 匹配第 n 个分组的子表达式,如果它经匹配。否则指的是八进制字符码的表达式。 |
Capture
(…) 正常分组,并捕获
(?:…) 分组,但是不捕获
>>> m = re.search(r'^(\d{3,4}-)?(\d{7,8})$','020-82228888') >>> m.group(0) '020-82228888' >>> m.group(1) '020-' >>> m.group(2) '82228888'
正则表达式修饰符
- re.M 正则表达式中的 re.M 表示将字符串视为多行,从而^匹配每一行的行首,$匹配每一行的行尾
Usages
文件目录操作
目录、文件获取
工作目录 脚本目录
#获取脚本运行目录 os.getcwd() #改变当前工作目录 os.chdir(new_work_dir) #获取脚本所在目录 os.path.split(os.path.realpath(__file__))[0] #获取路径的标准路径 全路径切其中不含有“./ ../”之类 os.path.realpath(a_abs_path) #获取 a_abs_path 路径相对于 b_abs_path 路径的相对路径 os.path.relpath(a_abs_path,b_abs_path) #windows 路径转为 linux 路径 a_path = os.path.realpath(a_path) a_path = a_path.replace("\\","/") ## 获取 HOME 目录 usr_home = os.path.expanduser(’~')
获取目录名 文件名
import os f = "a/b/c/d.txt" name, ext = os.path.splitext(f) print name, ext #a/b/c/d .txt print os.path.dirname(f) #a/b/c print os.path.basename(f) #d.txt
遍历目录下的文件和目录
file_dir_list = os.listdir(dir) for file_or_dir in file_dir_list: file_or_dir_abs_path = os.path.join(dir, file_or_dir) if os.path.isfile(file_or_dir_abs_path): ProcessFile(file_or_dir_abs_path) else: ProcessDir(file_or_dir_abs_path)
递归遍历目录中的文件
for parent_dir, dirs, files in os.walk(ccsproj_res_abs_path): for file in files: ProcessResFile(os.path.join(parent_dir, file))
递归遍历目录中的目录
for parent_dir,dirs,files in os.walk(ccsproj_res_abs_path): for dir in dirs: ProcessDir(os.path.join(parent_dir,dir))
判断目录 文件是否存在
os.path.exists(dir-or-file-full-path) os.path.isfile(file-full-path)
读写目录 文件
创建目录
os.makedirs(path) #多层目录 os.mkdir(path) #一层目录
读写文件
op_file = open("op.txt", "r") lines = op_file.readlines() op_file.close() op_file = open("op.txt", "w") op_file.write("You’re still goin’ strong") op_file.close()
修改文件编码
# python 编码相关的库 import chardet f = open(oldname) old_content = f.read() f.close() old_coding = chardet.detect(old_content)['encoding'] old_content = old_content.decode(old_coding) f = open(oldname, 'w') new_content = old_content.encode(new_coding) f.write(new_content) f.close()
修改文件名称
name, ext = os.path.splitext(file) newname = os.path.join(root,name+".md") os.rename(oldname,newname)
移动文件和目录
import shutil #移动文件(目录) shutil.move("oldpos","newpos")
复制文件和目录
import shutil #复制文件: shutil.copy("oldfile","newfile”) #oldfile 只能是文件,newfile 可以是文件,也可以是目标目录 shutil.copyfile("oldfile","newfile") #oldfile 和 newfile 都只能是文件 #递归 copy 目录下的所有文件和目录: shutil.copytree(src_dir,des_dir)
删除文件和目录
os.remove(file) #删除文件 os.rmdir(empty_dir) #删除空目录 os.removedirs(root_dir) #递归删除空目录 import shutil shutil.rmtree(root_dir) #递归删除目录下的所有文件和目录
压缩相关操作
zip
zip directory
import os import zipfile def ZipDir(src_dir_path, out_zipfile_path): if not os.path.exists(src_dir_path): print("source dir not exist! src_dir_path = " + src_dir_path) return zip_handler = zipfile.ZipFile(out_zipfile_path, 'w') source_dir_len = len(os.path.dirname(src_dir_path)) for parent_dir, dirs, files in os.walk(ccsproj_res_abs_path): for file in files: file_path = os.path.join(parent_dir, file) relative_path = file_path[source_dir_len:].strip(os.path.sep) zip_handler.write(file_path, relative_path) zip_handler.close() g_curPath = os.path.split(os.path.realpath(__file__))[0] ZipDir(g_curPath+"/testx", g_curPath+"/ttt.zip")
zip test password
zipfile
# -*- coding utf-8 -*- import argparse import zipfile def is_pwd_correct(archieve, some_file, pwd): is_correct = False try: file = zfile.open(some_file, mode="r", pwd=bytes(pwd, 'utf-8')) is_correct = True except: pass return is_correct if __name__ == "__main__": parser = argparse.ArgumentParser("--file <archive>" + "--dict <dictionary>") parser.add_argument( "-f", "--file", dest="archieve", required=True, type=str, help="Archieve file" ) args = parser.parse_args() print(args.archieve) zfile = zipfile.ZipFile(args.archieve, "r") print(is_pwd_correct(zfile, "test-zipcrack.txt", b"12332")) print(is_pwd_correct(zfile, "test-zipcrack.txt", b"123321"))
subprocess
sys_command_list = ["7z"] sys_command_list.append("t") sys_command_list.append("-p{}".format(pwd)) sys_command_list.append(archieve) result = subprocess.call(sys_command_list, stdout=subprocess.DEVNULL, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT) if result == 0: print("pwd = ", pwd)
7z
解析命令行参数
# 方案 1 from optparse import OptionParser parser = OptionParser(usage="%prog [options]") parser.add_option("-m","--machine",action="store",type="string",dest="machine",help="the machine to be check") parser.add_option("--OpenUnityProj", action="store", type="string", dest="unity_proj_path_arr", help="open multi unity projects!") (options,args)=parser.parse_args() if options.machine: print options.machine # 方案 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import sys def ShowHelper(): cmd_prefix = " python ./core_mgr.py " print("usage :") print(cmd_prefix+"-i #init core") print(cmd_prefix+"-i (ec)emacs-config #init core") print(cmd_prefix+"-i (se)spacemacs-elpa #init spacemacs-elpa") print(cmd_prefix+"-i (omz)ohmyzsh #init ohmyzsh") print(cmd_prefix+"-u #update core") print(cmd_prefix+"-u (se)spacemacs-elpa #update spacemacs-elpa") print(cmd_prefix+"-c #commit core") print(cmd_prefix+"-c (se)spacemacs-elpa #commit spacemacs-elpa") pass def main(): print(sys.argv) if len(sys.argv)<2: ShowHelper() else: opt_type = sys.argv[1] if opt_type=="-i": if len(sys.argv)==2: print("++++ START INIT MY CORE") #InitEmacs() #InitOhMyZsh() print("---- END INIT MY CORE") elif len(sys.argv)==3: opt_arg = sys.argv[2] if opt_arg=="ec": #InitEmacsConfig() pass elif opt_arg=="se": #InitSpacemacsElpa() pass elif opt_arg=="omz": #InitOhMyZsh() pass pass elif opt_type=="-u": print("UNSUPPORT -u!") elif opt_type=="-c": print("UNSUPPORT -c!") ## Logic Start if __name__ == "__main__": main()
Ftp 上传文件
class FTPClient(object): ''''' @note: upload local file or dirs recursively to ftp server ''' _DataTypeFILE = 'FILE' _DataTypeDIR = 'DIR' def __init__(self): self.ftp = None def __del__(self): pass def setFtpParams(self, ip, uname, pwd, port=21, timeout=60): self.ip = ip self.uname = uname self.pwd = pwd self.port = port self.timeout = timeout def initEnv(self): if self.ftp is None: self.ftp = ftplib.FTP() print '### connect ftp server: %s ...' % self.ip self.ftp.connect(self.ip, self.port, self.timeout) self.ftp.login(self.uname, self.pwd) print self.ftp.getwelcome() def clearEnv(self): if self.ftp: self.ftp.close() print '### disconnect ftp server: %s!' % self.ip self.ftp = None def uploadDir(self, localdir='./', remotedir='./'): if not os.path.isdir(localdir): return self.ftp.cwd(remotedir) for file in os.listdir(localdir): src = os.path.join(localdir, file) if os.path.isfile(src): self.uploadFile(src, file) elif os.path.isdir(src): try: self.ftp.mkd(file) except: sys.stderr.write('the dir is exists %s' % file) self.uploadDir(src, file) self.ftp.cwd('..') def uploadFile(self, localpath, remotepath='./'): if not os.path.isfile(localpath): return print '+++ upload %s to %s:%s' % (localpath, self.ip, remotepath) self.ftp.storbinary('STOR ' + remotepath, open(localpath, 'rb')) def __filetype(self, src): if os.path.isfile(src): index = src.rfind('\\') if index == -1: index = src.rfind('/') return FTPClient._DataTypeFILE, src[index + 1:] elif os.path.isdir(src): return FTPClient._DataTypeDIR, '' def upload(self, src, des='/'): filetype, filename = self.__filetype(src) self.initEnv() if filetype == FTPClient._DataTypeDIR: self.srcDir = src self.uploadDir(self.srcDir, des) elif filetype == FTPClient._DataTypeFILE: self.uploadFile(src, des+filename) self.clearEnv() def UploadFileOrDir(): appDirPath = g_projPath+"/build/"+g_platformType fileName = g_appName+"_"+g_buildNO localFilePath = "" remoteDirPath = "/GameDistribution/HDX_Dev/"+g_platformType+"/" if g_platformType == "PC": fileName = fileName + ".zip" elif g_platformType == "IOS": fileName = fileName + ".ipa" elif g_platformType == "Android": fileName = fileName + ".apk" localFilePath = g_projPath+"/build/"+fileName ftpClient = FTPClient() ftpClient.setFtpParams('dd-pc', 'sa', '') LogInfo("upload local file = " + localFilePath) LogInfo("upload remote dir = " + remoteDirPath) ftpClient.upload(os.path.realpath(localFilePath), remoteDirPath)
subprocess 使用
执行 svn 更新
import subprocess sys_command_list = ["svn"] sys_command_list.append("update") sys_command_list.append("xxx/my-svn-path") subprocess.call(sys_command_list)
获得文件夹属性
import subprocess result = subprocess.check_output("attrib "+folder,shell=True) result_list = result.decode("utf-8").split(' ')
面向对象编程
包
模块
# A.py AElem = 100 def BElem(): print("BElem") class CElem: def __init__(self): print("C init") # 1. 引用另一个文件 A.py 中的元素 AElem,元素 BElem import AElem from A import BElem from A import CElem from A # 2. 引用另一个文件 A.py 中的所有类 ## 方法 1 可以直接访问 A 中的元素 from A import * print(AElem) ## 方法 2 需要通过 A 来访问 A 中的元素 import A print(A.AElem) # 3. 通过 __all__ 定义导出的模块内容 __all__ = ['bar', 'baz'] waz = 5 bar = 10 def baz(): return 'baz' # 4. 从指定路径 import 模块 # https://stackoverflow.com/questions/67631/how-to-import-a-module-given-the-full-path # python 3.5 import importlib.util spec = importlib.util.spec_from_file_location("module.name", "/path/to/file.py") foo = importlib.util.module_from_spec(spec) spec.loader.exec_module(foo) foo.MyClass() # python 2 ## 方法 1 import imp gsvn = imp.load_source("gsvn", os.path.realpath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) + "/../gsvn.py") gsvn.update() ## 方法 2 import os import imp imp.load_source("log", os.path.realpath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) + "/../log.py") from log import * log_info("HelloWorld!") # 5. 错误的 import 模块 ## 在 A.py 父级目录中存在 D.py,下面代码出错的原因在于,相对路径 import 只对 package 有效 ## Error 1 : import ../D ## Error 2 : from ../D import * ## Error 3 : from .. import D
面向对象编程
python 的构造和析构函数为固定的名字。
构造函数--------------------- __init__( self ) 析构函数--------------------- __del__( self )
python 的静态成员 静态成员函数 普通成员函数
# 静态成员变量定义在类作用域中: class Test: static_var="" pass # 静态成员函数参数不含 self: @staticmethod def StaticFunc1(): ### pass # 静态成员函数参数不含 self, 包含 cls 方便调用其他静态函数: @classmethod def StaticFunc2(cls): cls.StaticFunc1() pass # 普通成员函数第一个参数为 self def MemberF(self): ### pass
python 的封装(private public protected)
# 私有的变量: ``` self.__pvar ``` # 私有的函数: ``` def __pfunc(self): ### pass
python 类的继承
class A: # 定义类 A class B: # 定义类 B class C(A, B): # 继承类 A 和 B
参考资料
Python 面向对象编程 http://www.runoob.com/python/python-object.html
MISC
- 脚本执行完暂停
import os os.system('pause')
异常处理
通用异常错误打印
try: subprocess.check_output(cmd_str, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, stdin=subprocess.PIPE) except Exception, e: print("ERROR: " + e)
subprocess 异常处理
try: subprocess.check_output(cmd_str, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, stdin=subprocess.PIPE) except subprocess.CalledProcessError, e: log_error("output = " + str(e.output))
Async Programming
Multi Threading
Multi Processing
创建 cpu core 数量的进程
# -*- coding utf-8 -*- import multiprocessing data_list = [] def process_data(lst, idx, NS): if idx == 45: NS.is_find = True NS.value = idx print(lst[idx]) if __name__ == "__main__": manager = multiprocessing.Manager() NS = manager.Namespace() NS.is_find = False NS.value = -1 cpu_core_count = multiprocessing.cpu_count() processor_count = max(2, cpu_core_count - 2) pool = multiprocessing.Pool(processor_count) for i in range(200): data_list.append("hi" + str(i)) print(multiprocessing.cpu_count()) for i in range(200): pool.apply( process_data, ( data_list, i, NS, ), ) print("============") pool.close() pool.join() print(NS) pass
multiprocessing pool apply vs apply_async
World-Excel 处理
安装使用的库
# 处理 word 文件的库 ## python2 安装 docx pip install docx ## python3 安装 python-docx pip install python-docx # 读 excel 的库 pip install xlrd # 写 excel 的库 pip install xlwt
docx
docx
import docx def get_docx(file_name): d = docx.opendocx(file_name) doc = docx.getdocumenttext(d) return doc doc = get_docx('tt.docx') print(doc) # 输出行数:1075 for d in doc[:5]: print(d) # 打印前 5 行 '''输出: 一、补益之剂 1.四君子汤 四君子汤中和义,参术茯苓甘草比 益以夏陈名六君,祛痰补气阳虚饵 除却半夏名异功,或加香砂胃寒使 '''
python-docx
import docx from docx import Document path = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\word.docx" document = Document(path) for paragraph in document.paragraphs: print(paragraph.text)
xlrd
xlwt
import xlwt wb = xlwt.Workbook(encoding = 'utf-8') ws = wb.add_sheet("Data", cell_overwrite_ok=True) ws.write(0,0,"row0 colum0 value") ws.write(1,0,"row1 colum0 value") ws.save("test.xls")
xlwt 写入 Excel 文件后,打开时提示文件后缀错误
xlwt 只能写 xls 文件,不能写 xlsm 文件,所以保存文件时,后缀名应该使用 xls
ValueError: column index (256) not an int in range(256)
xls 类型的文件,最大只支持 256 列,xlsm 文件可以支持更多列。改用 xlsmwriter 模块来实现写入 xlsm 文件。
https://www.cnblogs.com/z-x-y/p/9639702.html
xlsmwriter
安装
pip install XlsxWriter
使用
import xlsxwriter wb = xlsxwriter.Workbook("xxx.xlsx") ws = wb.add_worksheet() row_num = 1 for row_id,row in rows_dict.items(): ws.write(row_num, 0, row_id) for column_name,column_value in row.items(): if column_name not in g_column_info_dict: g_column_info_dict[column_name] = (g_column_counter, column_value[1]) g_column_counter = g_column_counter + 1 column_num = (g_column_info_dict[column_name])[0] ws.write(row_num,column_num, column_value[0]) row_num = row_num + 1 for column_name,column_info in g_column_info_dict.items(): column_num = column_info[0] ws.write(0, column_num, column_name+" "+column_info[1]) wb.close()
math
matplot
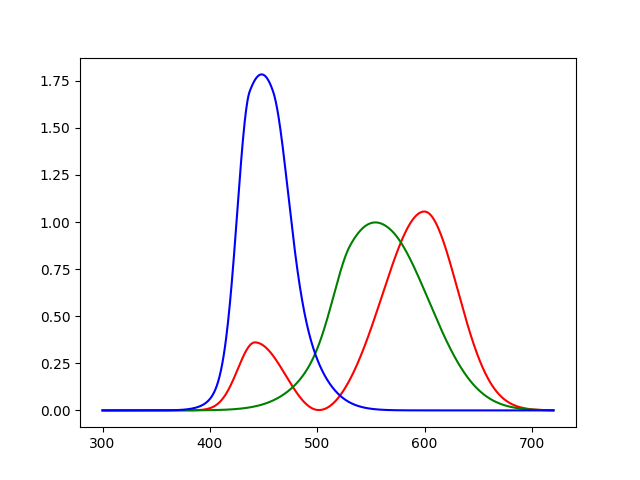
绘制分段函数
from scipy.integrate import quad import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np def g(x, u, t1, t2): if(x<u): return np.exp(-t1*t1 * (x-u)*(x-u) * 0.5) else: return np.exp(-t2*t2 * (x-u)*(x-u) * 0.5) def red(x): return 1.056*g(x,599.8,0.0264,0.0323) + 0.362*g(x,442.0,0.0624,0.0374) - 0.065*g(x,501.1,0.0490,0.0382) def green(x): return 0.821*g(x,568.8,0.0213,0.0247) + 0.286*g(x,530.9,0.0613,0.0322) def blue(x): return 1.217*g(x,437.0,0.0845,0.0278) + 0.681*g(x,459.0,0.0385,0.0725) # Data for plotting vred = np.vectorize(red) vgreen = np.vectorize(green) vblue = np.vectorize(blue) x = np.linspace(300, 720, 1000) yR = vred(x) yG = vgreen(x) yB = vblue(x) plt.plot(x, yR, 'r') plt.plot(x, yG, 'g') plt.plot(x, yB, 'b') plt.show() print("red =", quad(red, 300, 720)) print("green =", quad(green, 300, 720)) print("blue =", quad(blue, 300, 720))
numpy
matrix mult
np.array 可以定义行向量,也可以定义列向量
np.array 是按照行定义 matrix 的
np.matmul(a, b) 是 a matrix 右乘 b matrix, a 和 b 的顺序会影响结果
import numpy as np # glstate_matrix_projection glstate_matrix_projection = np.array( [ [3.1363900 ,0 ,0 ,0 ], # row0 [0 ,-2.7474770 ,0 ,0 ], # row1 [0 ,0 ,0.0015023 ,0.3004507], # row2 [0 ,0 ,-1 ,0 ] # row3 ] ) # test1 为行向量 test1 = np.array([1, 0, 0, 1]) # test2 为列向量 test2 = np.array([[1], [0], [0], [1]]) test1_proj = np.matmul(test1, glstate_matrix_projection) test2_proj = np.matmul(glstate_matrix_projection, test2) print("test1_proj \n",test1_proj) print("test2_proj \n",test2_proj) # test1_proj # [ 3.13639 0. -1. 0. ] # test2_proj # [[3.13639 ] # [0. ] # [0.3004507] # [0. ]]
NetworkX
# 安装 pip install networkx
colour
colour 基础
# 安装 colour pip install --user colour-science pip install matplotlib
- colour github https://github.com/colour-science/colour
- colour doc https://colour.readthedocs.io/en/develop/
plot matching function
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import colour #colour.plotting.plot_single_cmfs('CIE 1931 2 Degree Standard Observer') #colour.plotting.plot_single_cmfs('CIE 1964 10 Degree Standard Observer') colour.plotting.plot_single_cmfs('Wright & Guild 1931 2 Degree RGB CMFs') # 可用的matching function 如下 # Stockman & Sharpe 2 Degree Cone Fundamentals # Stockman & Sharpe 10 Degree Cone Fundamentals # Wright & Guild 1931 2 Degree RGB CMFs # Stiles & Burch 1955 2 Degree RGB CMFs # Stiles & Burch 1959 10 Degree RGB CMFs # CIE 1931 2 Degree Standard Observer # CIE 1964 10 Degree Standard Observer # CIE 2012 10 Degree Standard Observer # CIE 2012 2 Degree Standard Observer
spd xyz rgb convert
import colour import numpy as np cmfs = ( colour.MSDS_CMFS['CIE 1931 2 Degree Standard Observer'].copy().align(colour.SpectralShape(360, 780, 10)) ) illuminant = colour.SDS_ILLUMINANTS['D65'].copy().align(cmfs.shape) ## XYZ->SPD XYZ = np.array([1, 0, 0]) sd = colour.XYZ_to_sd(XYZ, method='Jakob 2019', cmfs=cmfs, illuminant=illuminant) colour.plotting.plot_single_sd(sd) ## SPD->XYZ sd = colour.sd_constant(100) print(colour.sd_to_XYZ(sd, cmfs, illuminant)) ## wavelength->XYZ print(colour.wavelength_to_XYZ(480, cmfs)) ## RGB->XYZ XYZ = np.array([0.7347,0.2653, 1-0.7347-0.2653]) illuminant_XYZ = np.array([0.34570, 0.35850]) illuminant_RGB = np.array([0.31270, 0.32900]) mat_XYZ_to_RGB = colour.RGB_COLOURSPACES['CIE RGB'].matrix_XYZ_to_RGB chromatic_adaptation_transform = 'Bradford' print(colour.XYZ_to_RGB(XYZ, illuminant_XYZ, illuminant_RGB, mat_XYZ_to_RGB, chromatic_adaptation_transform))
luminance radiance convert
plot SPD
## 显示SPD import colour sd = colour.sd_constant(100) colour.plotting.plot_single_sd(sd)
python graphics
pyopengl
# osx pip install PyOpenGL PyOpenGL_accelerate # windows ## 安装信息中会显示适合本机的pyopengl版本 pip install PyOpenGL pip install PyOpenGL_accelerate
测试是否安装成功
import numpy as np from OpenGL.GLUT import * from OpenGL.GL import * import ctypes VERTEX_SHADER = """ #version 330 layout (location = 0) in vec3 Position; layout (location = 1) in vec3 Color; out vec3 outColor; void main() { gl_Position = vec4(0.5 * Position.x, 0.5 * Position.y, Position.z, 1.0); outColor = Color; } """ FRAGMENT_SHADER = """ #version 330 in vec3 outColor; out vec4 FragColor; void main() { FragColor = vec4(outColor, 1.0); //FragColor = vec4(1.0, 0, 0 , 1.0); } """ def Create_Shader( ShaderProgram, Shader_Type , Source): ShaderObj = glCreateShader( Shader_Type ) glShaderSource(ShaderObj , Source) glCompileShader(ShaderObj) if glGetShaderiv(ShaderObj, GL_COMPILE_STATUS) != GL_TRUE: info = glGetShaderInfoLog(ShaderObj) raise RuntimeError('Shader compilation failed:\n %s'%info) glAttachShader(ShaderProgram, ShaderObj) def Compile_Shader(): global Shader_Program Shader_Program = glCreateProgram() Create_Shader(Shader_Program, GL_VERTEX_SHADER , VERTEX_SHADER) Create_Shader(Shader_Program, GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER , FRAGMENT_SHADER) glLinkProgram(Shader_Program) glUseProgram(Shader_Program) def Draw(): glClearColor(1, 1, 1, 1) glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT) glUseProgram(Shader_Program) glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO) glBindVertexArray(VAO) glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 3) glUseProgram(0) glBindVertexArray(0) glutSwapBuffers() def CreateBuffer(): vertex = np.array([[-1.0,-1.0,0.0], [1.0,-1.0,0.0], [0.0,1.0,0.0]],dtype="float32") color = np.array([[1.0,0.0,0.0], [0.0,1.0,0.0], [0.0,0.0,1.0]],dtype="float32") global VBO global VAO VAO = glGenVertexArrays(1) glBindVertexArray(VAO) VBO = glGenBuffers(1) glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO) glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertex.nbytes+color.nbytes, None, GL_STATIC_DRAW) glBufferSubData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0, vertex.nbytes, vertex) glBufferSubData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertex.nbytes, color.nbytes, color) posL = glGetAttribLocation(Shader_Program, "Position") colorL = glGetAttribLocation(Shader_Program, "Color") glEnableVertexAttribArray(posL) glEnableVertexAttribArray(colorL) glVertexAttribPointer(posL, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, None) glVertexAttribPointer(colorL, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, ctypes.c_void_p(vertex.nbytes)) glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0) glBindVertexArray(0) def main(): glutInit([]) glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_DOUBLE | GLUT_RGBA) glutInitWindowPosition(100, 100) glutInitWindowSize(500, 500) glutCreateWindow(b"HelloWorld") glutInitContextVersion(4,3) glutInitContextProfile(GLUT_CORE_PROFILE) glutDisplayFunc(Draw) glClearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0) Compile_Shader() CreateBuffer() glutMainLoop() main()
ERROR: PyOpenGL :: OpenGL.error.NullFunctionError: Attempt to call an undefined function glutInit, check for bool(glutInit) before calling
ERROR: in glutCreateWindow return __glutCreateWindowWithExit(title, _exitfunc) ctypes.ArgumentError: argument 1: <class 'TypeError'>: wrong type
// 将 glutCreateWindow("HelloWorld"); 改为下面方式 glutCreateWindow(b"HelloWorld");
pyvulkan
pip install vulkan # 测试是否安装成功 cd ~/Documents/MyProject/Test/vulkan_test git clone https://github.com/realitix/vulkan pip install pysdl2 pip install pysdl2-dll python ./vulkan/example/example_sdl2.py
Misc
python 版本管理器
pyen
如果已经安装了 python,可以将已经安装的 copy 到 d:/Applications/.pyenv/pyenv-win/versions 目录下,目录名称改为 python 版本号,便于识别不同版本。手动添加版本,需要执行如下操作
pyenv rehash
安装
Windows 版本安装请参考下面官方链接:
https://github.com/pyenv-win/pyenv-win
# 通过git安装 git clone https://github.com/pyenv-win/pyenv-win.git D:\.pyenv # 添加 PYENV PYENV_HOME PYENV_ROOT 环境变量 # D:\.pyenv\pyenv-win\ # 添加PATH环境变量 # D:\.pyenv\pyenv-win\bin # D:\.pyenv\pyenv-win\shims # 更新 pyenv cd D:\.pyenv git pull
OSX
brew install pyenv # 添加PATH环境变量 ## zsh 用户 echo 'export PYENV_ROOT="$HOME/.pyenv"' >> ~/.zshrc echo 'export PATH="$PYENV_ROOT/bin:$PYENV_ROOT/shims:$PATH"' >> ~/.zshrc echo 'eval "$(pyenv init -)"' >> ~/.zshrc ## bash 用户 echo 'export PYENV_ROOT="$HOME/.pyenv"' >> ~/.bashrc echo 'export PATH="$PYENV_ROOT/bin:$PYENV_ROOT/shims:$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrc echo 'eval "$(pyenv init -)"' >> ~/.bashrc ## fish shell 用户 # 配置 在shell中执行下面命令 set -Ux PYENV_ROOT $HOME/.pyenv set -U fish_user_paths $PYENV_ROOT/bin $fish_user_paths # 在 ~/.config/fish/config.fish 文件中添加如下两行 status is-interactive; and pyenv init --path | source pyenv init - | source
使用
# 查看可安装python的所有版本 pyenv install -l # 安装指定版本 pyenv install 3.9.4 # 查看当前版本信息 pyenv versions # 设置当前全局使用的版本 pyenv global 3.7.2 # 设置项目局部版本 pyenv local 3.7.2 # Alias 可执行文件(每次安装可执行文件后,都需要执行该命令) pyenv rehash
错误处理
pyenv Fatal error in launcher: Unable to create process using
# 执行下面命令,提示如题错误 pip install twisted # 使用下面命令代替上面命令 python -m pip install twisted
安装可执行文件后找不到
pyenv rehash
Windows: fish shell 中 调用 pyenv 命令错误
Windows: fish shell 中 调用 pyenv 命令都显示如下信息:
Microsoft Windows [版本 10.0.19045.2364] (c) Microsoft Corporation。保留所有权利。
需要 fish shell 支持 pyenv,当前 pyenv 可以在 msys2 shell 中正常使用。所以,只能暂时不在 windows fish shell 中使用 pyenv。
python 编辑器
PyCharm
参考 InitMyCore 中 InitJetBrainsIDE 部分的配置方法
emacs
参考 InitMyCore 中 python 部分的配置方法
spacemacs python
easy_install 安装插件
安装 Python 后,easy_install 默认会被安装到 C:Python\Python27\Scripts 目录下
# 切换到 eazy_install 所在的目录 执行下面命令 easy_install.exe xlrd
pip 安装更新卸载插件
安装 Python 后,pip 默认会被安装到 C:Python\Python27\Scripts 目录下
# 切换到 pip 所在的目录 执行下面命令 pip install pyinstaller # 更新 pip install -U pyinstaller # 卸载 pip uninstall pyinstaller # 查看colour-science 的所有版本 pip index versions colour-science # 强制安装某个版本 pip install --force-reinstall -v "colour-science==0.4.4"
指定 pip 安装源
# 零时指定安装源 pip install your-package -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple pip install numpy -i http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ # 永久修改默认安装源 pip config set global.index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple ## 国内的一些安装源 https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple #清华大学 https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ #阿里云 https://pypi.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/simple/ #中国科学技术大学 https://mirrors.cloud.tencent.com/pypi/simple #腾讯
Error 解决 ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'pip'
可以首先执行 python -m ensurepip 然后执行 python -m pip install –upgrade pip 即可更新完毕。
ERROR: After October 2020 you may experience errors when installing or updating packages. We recommend you use –use-feature=2020-resolver to test your packages with the new resolver before it becomes the default.
# 升级 pip python -m pip install --upgrade pip # 重新安装 packages pip install 'python-language-server[all]' # 检查 packages 引用是否有错误 pip check
离线安装插件
下载需要安装的插件
在线搜索并下载你需要的第三方库:网址 https://pypi.org/project/
安装插件
安装 whl 包:pip install **.whl(前提是要安装好 pip 和 wheel)
安装 tar.gz 包:cd 到解压后路径,python setup.py install(安装 pip 和 wheel 都可以参照这种方法)
将 python 脚本转化为 exe 可执行文件
# 打包 python 脚本 pyinstaller yourprogram.py # 打包 python 脚本为一个 exe 文件 pyinstaller -F make_proto.py # pyinstaller 文档 # Pyinstaller 用于打包 Python # 安装命令:pip install PyInstaller # 打包命令:pyinstaller -F -w myfile.py # 输入参数的含义: # -F 表示生成单个可执行文件 # -w 表示去掉控制台窗口,这在 GUI 界面时非常有用 # -p 表示你自己自定义需要加载的类路径,一般情况下用不到 # -i 表示可执行文件的图标 # Tips: # -F 命令生成的应用程序,在启动时会花很长时间。
修改 Python 脚本文件编码
#在文件前加下面代码: -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
python 中打印 package version
import colour from importlib.metadata import version version('colour')